Usability Evaluation:
Uber
By Rawan Bahmid
As most
people know, Uber provides a enhanced form of taxi service for which anyone can
be a driver. It provides private transportation options in such a way that
benefits both consumers and drivers. The company uses multiple media to deliver
its services [2].
We
evaluated its consumer mobile application to asses its learnability, simplicity
and discoverability. The evaluation was been performed on the Uber Android
application version 3.93.4, which was the latest available version for Android
5.1.1 when the evaluation started. Two evaluation techniques were used, heuristic evaluation using Nielsen’s 1990 [1]
principles and cognitive
walkthrough.
The evaluation covered three important tasks, to
determine the usability problems and difficulties that might face a user, to provide
some solutions, and ultimately to improve the user’s experience.
Task 1: Request Uber
This
feature allows the user to choose the car size, get the estimated fare and order a
car.
Success
scenario:
- Enter pickup location
- Choose UberX or UberXL
- Check car capacity
- Enter destination
- Tap GET FARE ESTIMATE
- Request Uber
- Choose payment method
- Enter promo code (if any)
- Confirm the request
Failure
scenario and recommendations:
Step 3, 4
& 5
Problem 1: the
choices are hidden in the bottom of the page, one has to scroll down to find
it, however, there is no sign or clue to scroll down. See Figure 1.
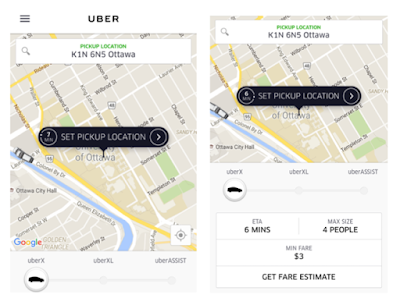 |
| Figure 1 Request Uber: Hidden options |
Issues of
hidden options in Step 3, 4 & 5 could be solved by making clear to the user
that there are more useful options in the bottom of the page. It would be
better if the maximum car capacity of people is shown graphically. And if more
expressive display of a currency sign is shown beside the text GET FARE
ESTIMATE.
Step 6
Problem 2: The
term SET PICKUP LOCATION is ambiguous and confuses the users. Should they enter
the the pickup location again which means the first entering was not
successful. But the address is in the PICKUP LOCATION field!! Or Is the entered
location not correct? Or it might be for confirming the entered location.
Problem 3: In
some times and places there are no available Uber cars. However, the user can
request a car and keep waiting for a request that would never be confirmed.
check Figure 2.
 |
Figure 2 Request Uber: No available car
|
Problem 4: In rush hours and when there is a lack of the available cars, a message would
show that there will be a surge pricing. User could choose NOTIFY ME IF SURGE
ENDS. However, user will not receive any kind of notifications even when the
surge ends, see Figure 3.
 |
| Figure 3 Request Uber: Surge pricing |
A clearer
and meaningful term should be used such as “REQUEST Uber” or “REQUEST CAR”.
Moreover, restrict the car requisitions to be used and activated only when cars
are available. And provide feedback or message to the user explain the
situation. Enhance the notification system as well.
Step 8
Problem 5: The
option seems to be inactive because it is gray and users might think it is restricted
and can not be used, see Figure 4.
Figure 4 Request Uber: Promo code
Better to colour the outline of the text to show that
it is active. And fill the text with a colour when a promo code is being used.
Problem 6: The
cars’ slider may confuse users; they might use to enter the addresses because
its like a path form a place to a place. They would first enter the Pickup
location, move the car to the next point and enter the destination.
This could
be solved by having radio button to chose the preferable car instead of the
slider. Check Figure 5.
 |
Figure 5 Request Uber: Redesign
|
Problem 7: Beside all the analyzed issues, the application only supports portrait orientation. It does not allow page rotation, which is helpful when following the car’s movement.
Task 2: Cancel a request
A car
request can be canceled before and after the completion of the request.
Scenario 1 illustrates the process of the cancelation before the request is
being completed. Whereas scenario 2 states the situation of cancelation when
the request has been completed.
Success
scenario 1:
- Hold X button to cancel
Failure
scenario 1 and recommendations:
Step 1
Problem 8: The
progress of the cancelation request is shown to the user, but it is not
confirmed when completed. After cancelation the confirmation of car request
page appears, which confuses the user as to whether or not the cancelation has been done.
To avoid this
confusion, provide descriptive feedback that states that the request has
been successfully canceled.
Success
scenario 2:
- Tap on CANCEL
- Confirm cancelation
Failure
scenario 2 and recommendations:
Step 1
Problem 9: The
CANCEL option is hidden. User has to scroll down to find it. However, there is
no clue that there are some available options further down the page. See Figure 6.
 |
Figure 6 Request Uber: Hidden CANCEL
|
Step 2
Problem 10:
No feedback is provided when the request is canceled. Therefore, user has to go
to the History page to make sure that the request has been canceled.
To allow
users to use this feature correctly, make the CANCEL button visible and
accessible by giving signal in the page that there are options when scrolling
down. Moreover, make sure to provide useful descriptive feedback when the
cancelation process is completed successfully.
Task 3: Add an address to Places
This
feature allows user to add their common to visit places to a list. Hence, they just
type the shortcut in the destination field when want going there, instated of
entering the full address.
Success
scenario:
- Main menu
- Tap Settings
- Tap Add HOME or Add WORK
- Enter destination
Failure
scenario and recommendations:
Step 3
Problem 11:
The list is very limited, only two addresses could be added to it. Moreover,
names of the places can not be changed. This is not expressive when adding,
for instance, the address of the university under the name HOME and will
require the user to remember each name is for what address. Check Figure 7.
 |
Figure 7 Add Places
|
Step 4
Problem 12:
When the address is correctly added to the list, no feedback is shown to the
user.
To make this
feature more useful, allow the user to enter as many address as they need and
name them based on their preferences. Furthermore, provide feedback when the
entered address has been added to the list. Figure
8 states a recommended redesign of the PLACES.
 |
Figure 8 Add Places: Redesign
|
Form the
analysis we can conclude that the issues of the application are because of the
invisible functions, limited options and the structural mistakes.
References
- Nielsen, J. & Molich, R. (1990). Heuristic evaluation of user interfaces. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '90), Jane Carrasco Chew and John Whiteside (Eds.). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 249-256.
- Uber (company). Wikipedia. Retrieved 20 March, 2016, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uber_(company)

Digital Marketing service , the promotion of products or brands via one or more forms of electronic media, differs from traditional marketing in that it uses channels
ReplyDelete